NBG HepatoShield and hemorrhagic fatty liver syndrome (HFLS) in laying hens
Dear colleagues,
This week, our article analyzes the hepatoprotective effects of enhanced silymarin (NBG HepatoShield) in laying hens.
Silymarin is a flavonolignan compound derived from milk thistle seeds (Silybum Marianum) with hepatoprotective properties due to its antioxidant effect on liver metabolism, helping to replenish glutathione reserves used by hepatocytes to fuel glutathione peroxidase GPTx function.
In addition, silymarin appears to stabilize cell membranes, scavenge free radicals, and stimulate protein anabolism in the liver.
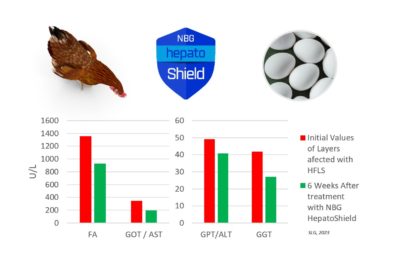
As a result of its activity, levels of aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) are reduced.
As we have already mentioned, NBG has enhanced the effect of silymarin with NBG Bioboost technology, creating the product NBG HepatoShield.
As a result, we have been able to reverse the symptoms of fatty liver disease in laying hens by reducing FA, ALT, AST, and GGT levels by up to 43%.
Hemorrhagic fatty liver syndrome (HFLS) is a disease characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver, leading to liver rupture, hemorrhage, and sudden death in birds. Affected animals can suffer significant economic losses due to mortality and decreased egg production and shell quality.
Finally, here is an article that shows the hepatoprotective effects of silymarin in birds:

